2.3 The Gas Chromatograph
The main purpose of chromatography is to separate a complex mixture of compounds into discrete chromatographic peaks containing only one analyte. Today’s capillary column chromatographic systems are ideal for this task and interface well with detection by mass spectrometry due to the low volume of carrier gas used in capillary columns (1 to 5 mL/min as opposed to 60-100 mL/min in packed column GC used prior to the 1980s). Figure 2.5 below, illustrates the major components of a modern capillary column gas chromatograph – mass spectrometry (GC-MS) system.
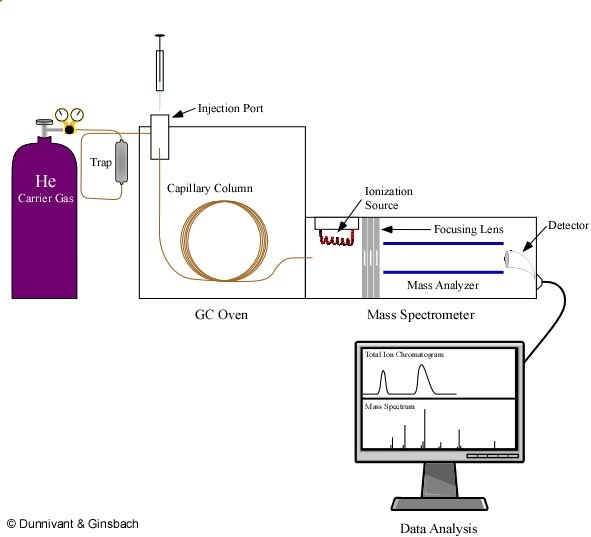
Figure 2.5. A GC-MS System
| Frank's Homepage |
©Dunnivant & Ginsbach, 2008