4.5.1 UV-Vis Spectrophotometry
UV-visible absorption is the most common detection technique for CE. Detection is nearly universal, and with fused-silica as the sample holder, wavelengths from 200nm through the visible spectrum can be used without interference. Generally, the capillary itself is used as the sample holder and passes through a UV-vis detector.
Because the capillary tube is so thin compared to conventional path lengths, care needs to be taken in the design of the detector. The beam of light must be of small radius and focused directly on the capillary for accurate results. A disadvantage of this is that, correspondingly, few photons reach the detector and a generally high baseline is obtained. The optical beam is generally passed through a slit to restrict its width and center it on the capillary tube.
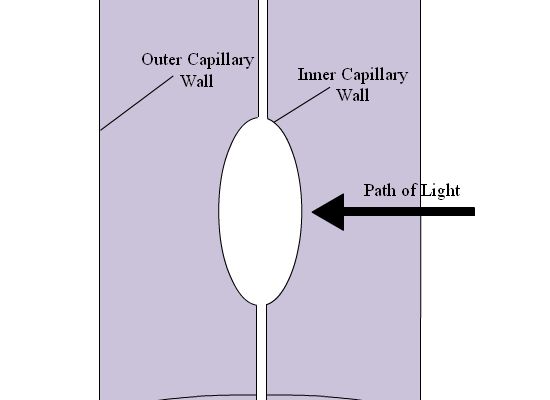
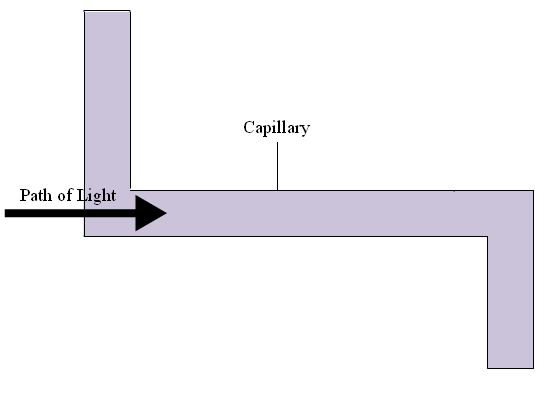
One approach to decrease the detection limit is by increasing the path length of the flow cell. This can be done by increasing the diameter of the capillary, but by doing this there is also an increase in the current and resulting Joule heating. Two ways of increasing path length without increasing capillary diameter are depicted in Figure 4.10. The method shown in 4.10A, called the “bubble cell” does not require an increase in current, as the detection occurs after separation. When a zone enters the bubble, the velocity decreases as it expands to fill the capillary, it contracts along the capillary and overall concentration remains the same, even with increasing path length. There is a third method, which is a combination of 4.10a and 4.10b; the capillary bends to increase the path length, but the capillary is also bubbled along the path.


4.10: a) Capillary bubble cell for UV-Vis detection; b) capillary cell.
When trying to detect a given analyte, care must be taken to ensure the running buffer is not optically active in the range of the analyte. Most peptides and carbohydrates absorb around 200nm, and consequently many biological buffers, such as HEPES, CAPs, and tris, should not be used in systems analyzing peptides and carbohydrates.
A normal S/N for a 75mm id capillary is 62.5, and up to 650 on an increased path length cell.